The cricoid cartilage is an annular structure in the larynx’s caudal region. It is a key anatomical feature that provides necessary structural support for the larynx. It is a vital organ responsible for respiration and speaking.
In addition, it is a critical anatomical landmark for various medical procedures, including endotracheal intubation. A tube is inserted into the airway through the oral or nasal cavity to facilitate ventilation.
Medical conditions affecting the cartilage, including neoplastic, traumatic, and inflammatory conditions, can cause significant respiratory distress.
If this happens to you, you may require medical intervention.
Helpful content: Can Drinking Hot Water Shrink Fibroids?
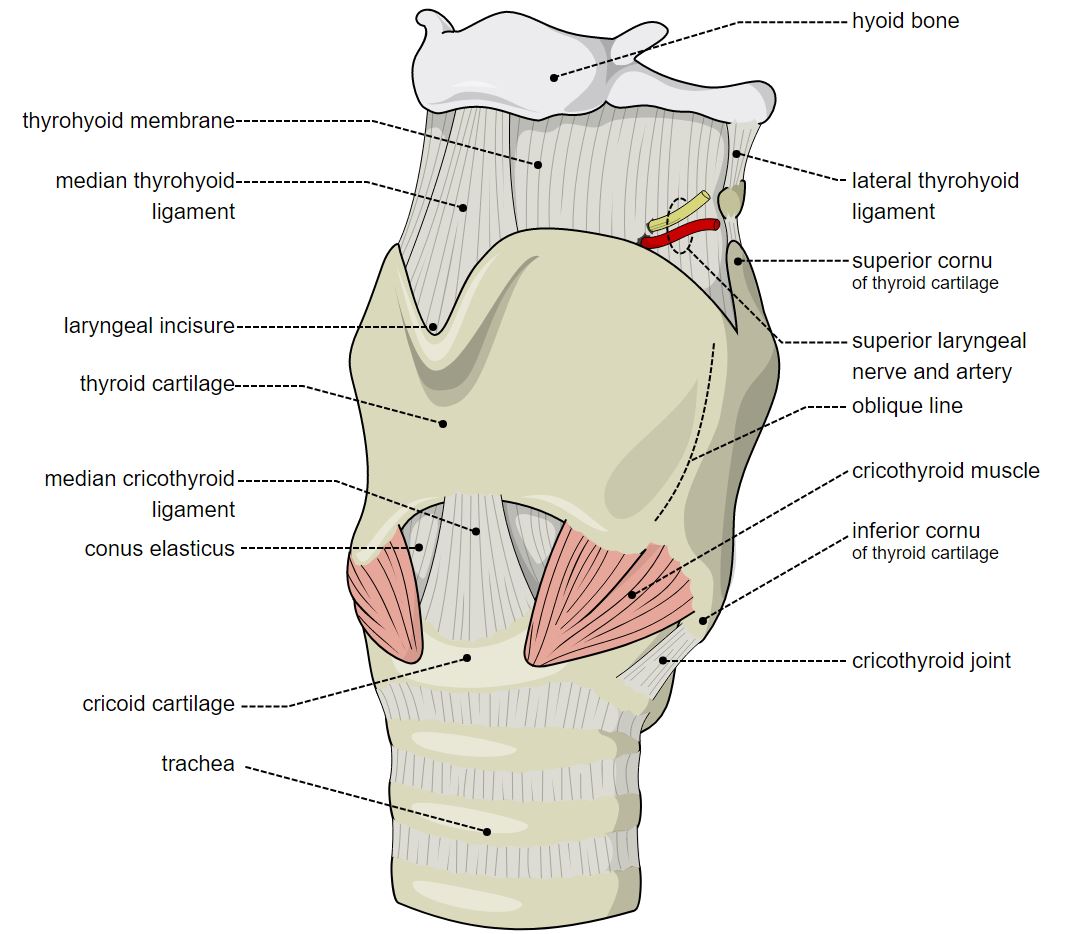
Cricoid Cartilage Location
Cricoid cartilage encircles the trachea – the airway that leads from the larynx to the bronchi – and composes the interior-most boundary of the laryngeal skeleton.
It sits just below the pharynx and is a part of the larynx.
It sits at the level of the C6 vertebra.
Cricoid means ring-shaped. Cartilage is a connective tissue.
Cricoid Cartilage Functions
The cricoid cartilage plays a crucial role in both breathing and speaking.
- It provides the larynx with a structure.
- It gives stability to the laryngeal framework during breathing.
- The cartilage helps maintain an open airway.
- It prevents laryngeal collapse, which is crucial for proper breathing.
- This cartilage is also essential for producing sound and speech.
Anatomy of Cricoid Cartilage
It is ring-shaped and stays at the base of the larynx.
It has a wider posterior lamina and a smaller anterior arch, both of hyaline cartilage.
Cartilage cells are called chondrocytes. These cells release substances that make it strong yet flexible.
The cricoarytenoid joints link the posterior lamina to the arytenoid cartilage and the anterior arch to the thyroid cartilage, allowing for movement of the vocal cords during phonation.
Its unique shape and position make it crucial during medical emergencies, providing a secure anchor point for inserting an endotracheal tube.
Helpful content: What are Bedoyecta Injections?
Parts of Cricoid Cartilage
It has two important parts:
- Lamina. About 3cm
- Arch. Amout 7mm.
It also has two borders:
- Upper border, which runs upward and backward.
- Lower border. It is horizontal and connected to the trachea.
Helpful content: What is Skin Irritation ICD-10?
Types of cartilage
There are three main types of cartilage. They are:
- Hyaline cartilage. It makes the embryonic skeleton.
- Fibrocartilage. They are tissues found mostly in intervertebral disks. However, they are also found at the insertions of ligaments and tendons.
- Elastic cartilage. They make up the external part of our ears external ear and the auditory tube of the middle ear.
Medical Conditions that Affect Cricoid Cartilage
Several medical conditions can affect the cricoid cartilage. They include:
Trauma
Blunt or penetrating trauma to the neck can cause fractures or dislocations of the cartilage, leading to airway obstruction and difficulty breathing.
Neoplastic conditions
Tumors that develop in or around the cartilage can cause airway obstruction and respiratory distress. These tumors can be benign or malignant.
Inflammatory conditions
Cartilage inflammation, such as in the case of laryngotracheobronchitis, can cause airway narrowing and difficulty breathing.
Autoimmune conditions
Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders can cause inflammation to the cricoid cartilage, leading to airway obstruction and difficulty breathing.
Infectious conditions
Infections like tuberculosis or syphilis can destroy the cricoid cartilage, leading to airway obstruction and respiratory distress.
Congenital abnormalities
Some individuals may be born with structural abnormalities of the cricoid cartilage that can cause airway obstruction and respiratory distress.
Various medical conditions can affect the cartilage and compromise respiratory function. Prompt recognition and management of these conditions are critical to ensuring optimal outcomes and preserving airway patency.
Is cricoid cartilage painful to touch?
Cricoid cartilage can be painful to touch.
That happens especially if you have undergone trauma and fractured your cartilage.
The pain may also come from a tumor called Chondroma.
Conclusion
The cricoid cartilage is a crucial component of the larynx. Its unique shape and position make it vital for medical procedures such as intubation, while its association with the recurrent laryngeal nerve underscores its importance in preserving laryngeal function.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the cricoid cartilage is critical for diagnosing and managing laryngeal disorders and improving patient outcomes.
FAQ
The cricoid cartilage itself does not contain muscles. However, it works as a connective point for other muscles. Those muscles are engaged in helping you speak. At the same time, its arch serves as the origin for the bilateral lateral cricoarytenoid muscles.
The answer is no. The cricoid cartilage of men ranges from 11.0 to 21.5mm. For women, the range is between 8.9 to 17.0 mm.
Additional Info
- National Library of Medicine
- Encyclopedia Britannica
- IMAIOS